The adoption of cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions has gained significant traction in recent years, with SAP S/4HANA Cloud emerging as a frontrunner. This cloud-based solution, particularly its public cloud edition, offers businesses enhanced agility and streamlined operations. However, the shared infrastructure and multi-tenancy environment of the public cloud introduce unique challenges for auditing this system.
In this blog, we’ll unravel the intricacies of auditing SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Public Edition, offering insights and strategies for a comprehensive audit.
Understanding SAP S/4HANA Cloud Ecosystem
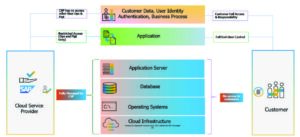
A thorough understanding of the SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud ecosystem, particularly its unique structure and shared responsibility model, is crucial for ensuring compliance with industry standards and serves as the foundation for effectively auditing your SAP application security procedures. This cloud-native platform simplifies multi-cloud and hybrid system landscapes by offering automated processes for tasks like server and storage provisioning, operating system management, database software maintenance, and optimisation. However, the shared infrastructure and multi-tenancy environment inherent in the public cloud require a deeper understanding before diving into the audit itself. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of this requires mapping your cloud environment’s components (provider, infrastructure, applications, and data) to identify critical touchpoints for security and compliance assessments.
A typical public cloud deployment follows a layered architecture comprising infrastructure, platform, and application components:
- Infrastructure: The infrastructure layer consists of computer, storage, and network resources. These resources are provisioned from the public cloud provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform: The platform layer consists of software that provides services such as application deployment, runtime management, and security. These services are provided by the public cloud provider or by third-party vendors.
- Applications: The applications layer consists of the SAP applications that are deployed to the public cloud. These applications can be either SAP on- premises applications that have been migrated to the public cloud or new SAP applications that have been developed specifically for the public cloud.
The Shared Responsibility Model
In the cloud environment, the responsibility for security and compliance is shared between the cloud provider and the customer. The cloud provider bears responsibility for the security of the underlying infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing the applications and data, they deploy on the cloud platform. This shared responsibility model necessitates a collaborative approach to auditing, with both parties contributing to a comprehensive assessment.
The specific responsibilities of SAP and customers vary depending on the deployment model and the specific services being used. In SAP S/4HANA Cloud, customers have no access to the lower-level infrastructure layers such as virtual machines, operating systems, load balancers and networking configuration as SAP manages them. A shared responsibility model requires collaboration to ensure a secure and compliant cloud environment for your SAP applications.
Once you understand your cloud architecture, you can implement security measures, compliance controls, and performance optimisation strategies for your SAP application security. While SAP safeguards the application and underlying infrastructure in their public cloud S/4HANA offering, the ultimate responsibility for securing your data and adhering to relevant compliance regulations lies with you, the customer.
Your responsibilities include:
- Securing your customer data: Configure authentication methods like multi-factor authentication, authorisation levels through role-based access control (RBAC), and secure integration practices.
- Managing business processes and workflows: Maintain control over the logic and flow of your applications within the cloud environment.
- Managing user identities and access: Create and manage user accounts, assign appropriate access permissions based on their roles, and implement strong authentication protocols.
- Handling consent management: Obtain and manage user consent for data collection and processing as required by regulations.
- Monitoring security audit logs: Regularly review logs like user logins, failed authentication attempts, and system events to identify and address potential security threats.
To implement and audit these areas in your SAP applications, there are several tools and techniques available. However, the specific approach may vary based on your unique needs and resources.
Conducting regular audits in the SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud is an ongoing process crucial for ensuring the security of data and systems. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited budgets and resources, audits can be a significant investment in terms of time and cost.
Outsourcing SAP application security audits to third-party providers can be a strategic option for SMEs to maintain a robust security posture while efficiently managing costs and resources. However, it’s essential to carefully evaluate different providers and choose one that aligns with your specific needs and budget.
Auditing SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Public Edition poses distinctive challenges due to the shared infrastructure and multi-tenancy inherent in the public cloud. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution, demanding a holistic understanding of one’s cloud architecture, proactive vigilance in security, and commitment to SAP security compliance.
As businesses transition to the public cloud, establishing a robust audit framework for SAP application security simplifies the process. Embracing a comprehensive approach that considers these factors and leverages appropriate tools and resources like outsourcing SAP application security audits to third-party providers, emerges as a cost-effective solution for SMEs with limited budgets.
In essence, a well-executed and continuous audit process is not just a regulatory necessity but a strategic necessity for businesses adopting cloud-based ERP solutions.
It ensures the resilience and security of SAP applications in the ever-evolving landscape of SAP security compliance.
If you’d like to know more, get in touch with our experts.