In this blog, we would like to provide our readers an overview of all 3 of the SAP GRC applications – AC/PC/RM. The GRC suite is a set of applications aimed to minimize the cost of compliance through automation of compliance tasks, manage governance and comply with regulations. For Process Control and Risk Management, it is a multi-compliance framework that helps customers to comply with different regulations in one single environment.
SAP Access Control
SAP Access Control helps companies to identify, monitor and prevent access risk. It has a set of tools to secure, control access, and prevent fraud across complex landscapes. The application consists of 4 modules:
- Risk Analysis and Remediation – Run risk analysis to detect access risk violations across systems. Mitigate risks using Mitigating controls and report on your current risk situation.
- Compliant User Provisioning – Flexible workflow configuration allows creation of different workflow paths with different stages of approvals. End Users become capable of creating their own requests (system access or superuser access). Using capabilities such as User Access Review, the reviews of user access, role authorizations and risk violations become an automated task.
- Business Role Management – BRM is the repository of roles. Business roles can be defined according to job/function which makes it easier for business users to understand. A role methodology is available which enables consistency through role design and helps customers to create and maintain risk free roles.
- Emergency Access Management – The application gives temporary access to users who need to execute critical functions outside of their function scope. It makes users accountable for their actions as the access is tracked and monitored. Log reports are available to analyse user activity.
SAP Process Control
Companies must comply with regulators and a Non-compliance can result in penalties. SAP Process Control helps companies to ensure compliance by managing internal controls. It is a combination of lots of different frameworks translated into one single application. Highly regulated industries and complex organisations makes it hard to track and monitor risks. If the audit process is inefficient, it raises the chances of high risks. Controls are created and monitored using a central catalogue. By conducting assessments and tests techniques on controls, issues and remediation plans can be tracked and make sure their control environment is documented and transparent. A large set of tools is available to report, certify and automate the company`s key controls.
SAP Risk Management
Minimize company losses from high impact events using Risk Management application. Enterprise risk can be analysed in different ways and monitored on a continuous basis using Key Risk Indicators. Analytical dashboards and reports are available for stakeholders to be able to mitigate risks in their areas of responsibility or to upper management to have a broad visibility on the company`s risks.
Integration
Access Control + Process Control
Access Control and Process Control integration is based on the activation of both modules. If Access Control and Process Control are activated in the system, the mitigating control in AC becomes an internal control in PC. Segregation of Duties controls become available to execute SOD reports based on a business rule. By leveraging Access Control solution SOD rules (SAP GRC SOD violations, critical actions and critical permissions), Process Control automates periodic SOD reports and raise issues in case it finds exceptions in the business rule criteria. An exception would mean a detection of an issue.
Process Control + Risk Management
Process Control integrates with Risk Management via Risk Harmonization. To avoid limited visibility of risks, risks from Risk Management can be directly assigned into controls from Process Control Application. At the same time, the control is assigned to the risk as a risk response. If a PC control is assigned to a risk in Risk Management, the risk is added to the control in Process Control. The following diagram explains this process:
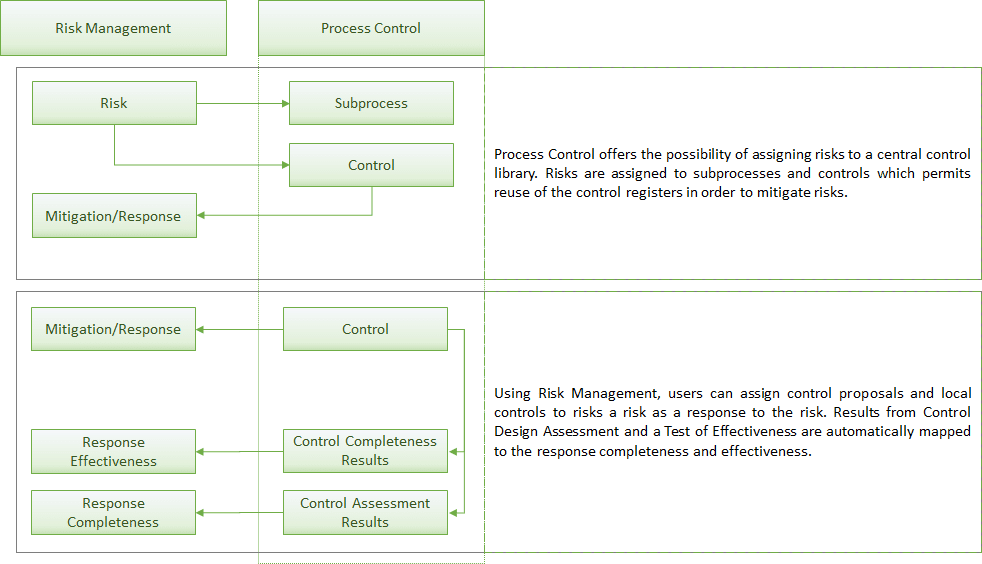
With or without risk harmonization enabled:
- Risk Templates can be associated to Subprocesses and Controls
- Completeness and Effectiveness of the response will still be updated by controls tests and assessments



